Search
The semiconductor manufacturing industry is classified as an "extremely high-risk" industry by the United States (FMS) organization due to the use of highly toxic, corrosive, and flammable gases, liquids, and a large amount of flammable plastic materials in the process, as well as the enclosed working environment and gas pump system in dust-free rooms. As a user of gas in semiconductor wafer foundries, every staff member should understand the safety data of various hazardous gases before use and know how to deal with emergency procedures in case of gas leakage.
There are a large number of ultra-fine gas pipelines in the semiconductor industry production rooms, and after installation, they must go through strict testing before they can be put into normal use. The five essential analysis tests for ultra-fine gas pipelines are: pressure/ammonia leakage/dust content/moisture and oxygen analysis detection. Only when all five tests meet the standards can the factory be put into use, otherwise there will be great potential safety and economic risks.

According to the relevant provisions of the current national standard "Technical Specification for Special Gas System Engineering" GB50646-2011 and "Technical Conditions and Inspection Methods for Toxic Gas Detection and Alarm Devices" HG23006, and combined with the fast response requirements for gas detection devices used in semiconductor factories, the detection and alarm response time is specified. Require the installation of toxic gas detectors and systems at exhaust outlets or environmental points. If any toxic gas leakage occurs, it will be detected by the gas detection system. This control system will determine the relevant interlock actions of the entire gas delivery system based on the magnitude of the harm to human health caused by gas leakage. In severe cases, all upstream gas sources will be urgently shut off, and the central control room and on-site alarm system will be driven, It may even drive the entire factory's automatic voice broadcasting system to notify immediate evacuation and require relevant personnel to quickly evacuate the alarm area. Therefore, as long as engineering and technical personnel strictly follow the established standard operating procedures, all these safety devices will ensure that personnel do not have safety concerns.
Main gas detection in the semiconductor industry
Carbon monoxide (CO), ammonia (NH3), oxygen (O2), hydrogen chloride (HCl), chlorine (Cl2), hydrogen fluoride (HF), phosphine (PH3), and hydrogen (H2) are toxic, harmful, flammable, and explosive gas sensors. They are professional level sensor products designed for toxic gas monitoring applications in the semiconductor manufacturing industry. The sensor has a long lifespan and can be stably and continuously monitored for a long time, which can greatly reduce the cost of toxic gas monitoring in the semiconductor manufacturing industry, achieve large-scale installation and application, and provide a practical and feasible safety production monitoring solution for toxic gas monitoring in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
|
No. |
Measurement Gas |
chemical formula |
Measurement range |
|
1 |
ammonia |
NH3 |
0-100 ppm |
|
2 |
carbon monoxide |
CO |
0-100 ppm |
|
3 |
Oxygen |
O2 |
0-100% |
|
4 |
chlorine |
CL2 |
0-20 ppm |
|
5 |
Hydrogen chloride |
HCL |
0-100 ppm |
|
6 |
phosphine |
PH3 |
0-10 ppm |
|
7 |
hydrogen |
H2 |
40-4000 ppm |
Common types of hazardous gases in semiconductor and electronic factories
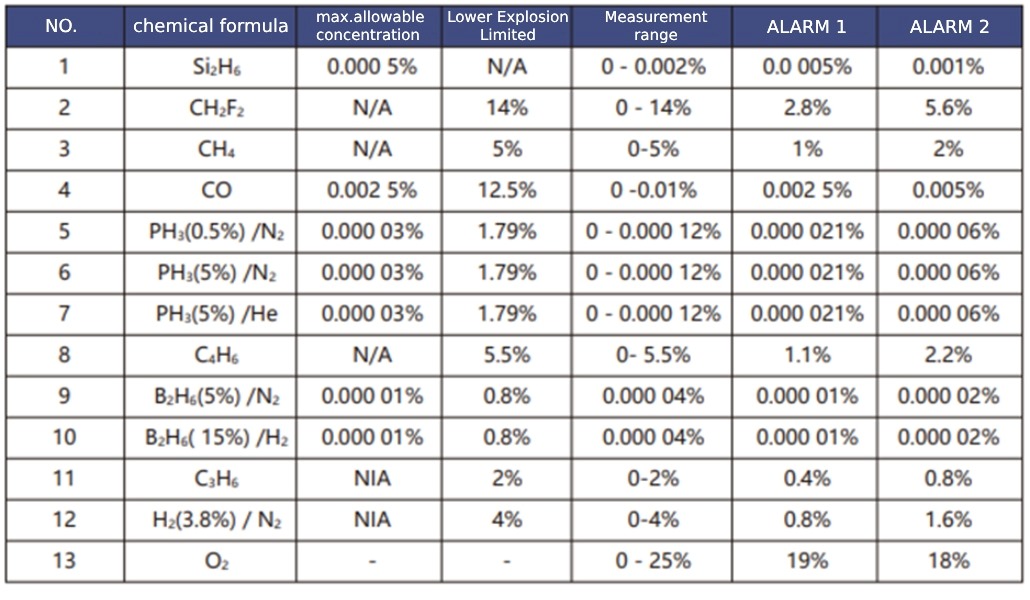
Gas detection and monitoring system for semiconductor electronic factory buildings
In the processing of semiconductor and electronic factories, the use of highly hazardous substances, especially combustible gases, toxic gases, and other gases, is increasing day by day. Inevitable gas leakage incidents occur occasionally, which in turn pose potential hazards to factories, their employees, nearby residents, and the environment. The global incidents of combustion, explosion, suffocation, and casualties caused by gas leaks constantly remind people of the existence of this problem. Gas detection and monitoring systems have emerged with the aim of early and timely detection and warning of gas leaks, helping people to have more time to prevent and take remedial actions.
At present, there are more than 110 types of special gases applied in the semiconductor industry, with 20-30 commonly used, accounting for up to 14% of the raw material demand.
Common gas detection applications in the semiconductor industry:

SIGAS provides gas concentration quantification and control equipment and one-stop solution for the semiconductor industry, as well as control equipment for toxic and harmful gases such as carbon monoxide CO, ammonia NH3, oxygen O2, hydrogen chloride HCl, chlorine Cl2, hydrogen fluoride HF, phosphine PH3, and hydrogen H2, such as sensors, alarms, and transmitters, to safeguard the front-end production process of semiconductors.